Diseases of the endocrine system are diverse. They are easy to diagnose with the right diagnostic equipment, but quite challenging in terms of treatment or correction of balance in the body.
Diagnostics
Most endocrine diseases can lead to significant health problems and a number of complications, such as infertility, decreased visual acuity and blindness, impaired ability of the tissues to regenerate and reduce the body’s resistance to infections.
For accurate diagnosis are:
- determination of hormone levels in the blood plasma;
- tests for chromosomal and genetic disorders;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography;
- needle biopsy study taken from the body cells;
- ultrasound diagnosis.
If there is suspicion of tumor in the endocrine glands, it is also can be used positron emission tomography, the definition in the blood of certain tumor markers and other necessary tests.
Treatment
Treatment of endocrine diseases is chosen individually for each patient in order to impact not only on the problem of the body, but also on other organs and systems, which could be seriously affected by imbalances in the body.
Used for the treatment of:
- selection of diet, physiotherapy, balneotherapy, herbal therapy, therapeutic exercises;
- the use of drugs that compensate for the lack synthesized by endocrine glands substances;
- surgical methods of treatment using endoscopic techniques.
In endocrinologica offices Israeli hospitals can be tested and get help in such seemingly simple cases, such as obesity, when one does not help the ordinary diet and exercise.
Clinics in this area
News and articles of medicine Israel
Imaging the effects of hunger on the brain’s response to food cues
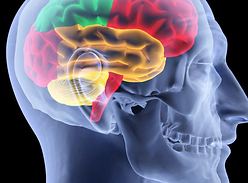
Our brain pays more attention to food when we are hungry than when we are sated. Now a team of scientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) has shed light on how the needs of the body affect the way the brain processes visual food cues.
Study provides insight into how weight-loss drug acts in the brain

A weight-loss drug dampened the response to food cues in regions of the brain associated with attention and emotion, leading to decreases in caloric intake, weight and body mass index (BMI), a team led by scientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) reported.
Diabetes: Key to faster-acting insulin found in snail venom

A study of the crystalline 3-D structure of an insulin extracted from the venom of a marine snail reveals a potential way to make insulin for the treatment of diabetes act more rapidly.
Type 2 diabetes: Gene discovery could yield new treatments
Researchers from the United Kingdom have discovered a gene that aids the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, contributing to type 2 diabetes.
Compact insulin pump from the company ToucheMedical

Among patients with a diagnosis of diabetes, Parkinson disease, thalassemia increased demand special pumps for subcutaneous administration of essential medicines. The devices with the computer control system are an alternative to syringes or syringes-handles for injection of insulin and other drugs. The pump consists of a flexible needle (cannula), thin hoses, pump the size of a pager.